How to Use ChatGPT 4o's Update to Turn Key Insights Into Clear Infographics (Prompts Included)
This 3-step workflow helps you break down books, reports, or slide-decks into professional visuals that accelerate understanding.

What if turning any idea into a crystal-clear visual was as simple as a single prompt?
Until recently, AI-generated images were more magic trick than a serious thinking partner.
Fun, sure.
But often, full of noise.
You’d ask for “an infographic about learning how to learn,” and get spaghetti fonts and nonsense icons.
But on March 25, 2025 something shifted.
My testing of the latest GPT-4o update started as casual curiosity and spiraled into a full-blown deep dive. I tried all kinds of prompts and use cases (more to come) built on the science of learning.
With books, scientific papers, and even slide decks.
I wrote dozens of prompts, refined the language, and built a repeatable method.
I grounded it in two learning science theories—Dual Coding Theory1 and Cognitive Load Theory2—which explain how visuals facilitate learning.
The result?
A 3-step process that turns dense content into crystal-clear infographics.
This article shows you how to find core ideas, prompt GPT-4o3 for a design brief, and generate clean, professional images that stick. These aren’t vague “creative visuals”—they’re structured for learning, memory, and action.
If you’re a lifelong learner, educator, creator, or just someone who wants to work smarter, this process is for you.
You’ll spend less time re-reading and more time understanding. nd maybe—just maybe—you’ll build ideas that not only click in your brain, but also stick in someone else’s.
Let’s break down how to use GPT-4o’s image generation to turn complex reports, academic papers, or long books into one-glance visuals your brain will find easier to remember.
Image Generation That’s Actually Useful
We’ve seen AI make surreal art before. But beautiful isn’t always helpful for learning.
The latest ChatGPT 4o update changes the game because image generation is integrated directly within the chat context. You can move seamlessly from "describe what you want" to "see what you mean."
Here’s why this is a leap forward for learners:
🧠 Context: Generate visuals inside your conversation. Your diagram or explainer image pulls directly from your chat context—no clumsy exporting/importing or re-explaining needed.
✍️ Text: These models handle text within images much better (labels, signs, code snippets) because they treat text and image as deeply interconnected.
🛠️ Refinement: Ask for edits. Change the style. Zoom out. Layer in knowledge. Multi-turn generation means the model remembers what you’re building—and helps you refine it as you go within the chat.
💡 Reasoning: The visuals are informed by the GPT-4o’s knowledge and reasoning ability. Your infographic makes logical sense.
So let’s look at the three steps.
Step 1: Extract core ideas from input material
First, upload the book, PDF, or article you want to create an infographic for in GPT, and use this prompt (interestingly, it has been working better for me than a more sophisticated 5-step prompting guide).
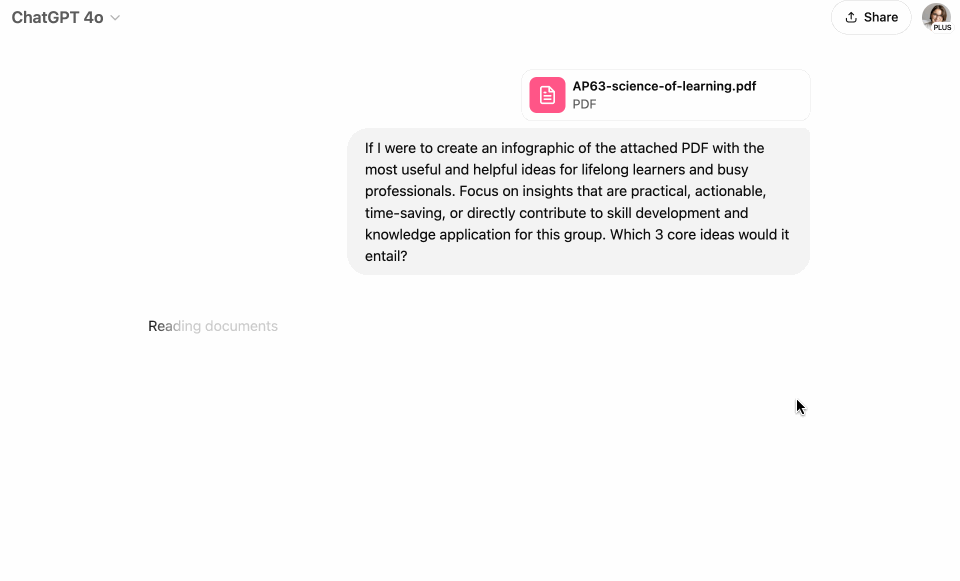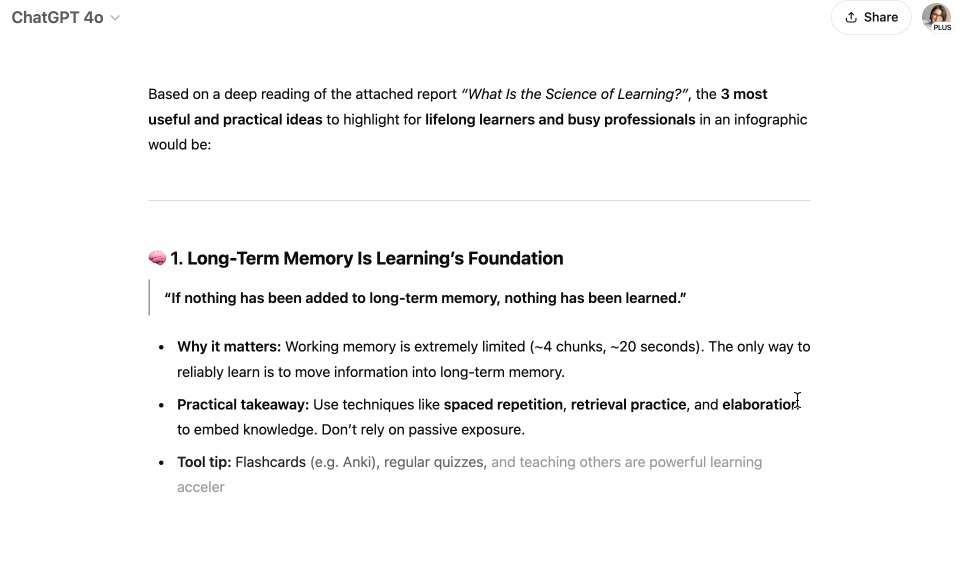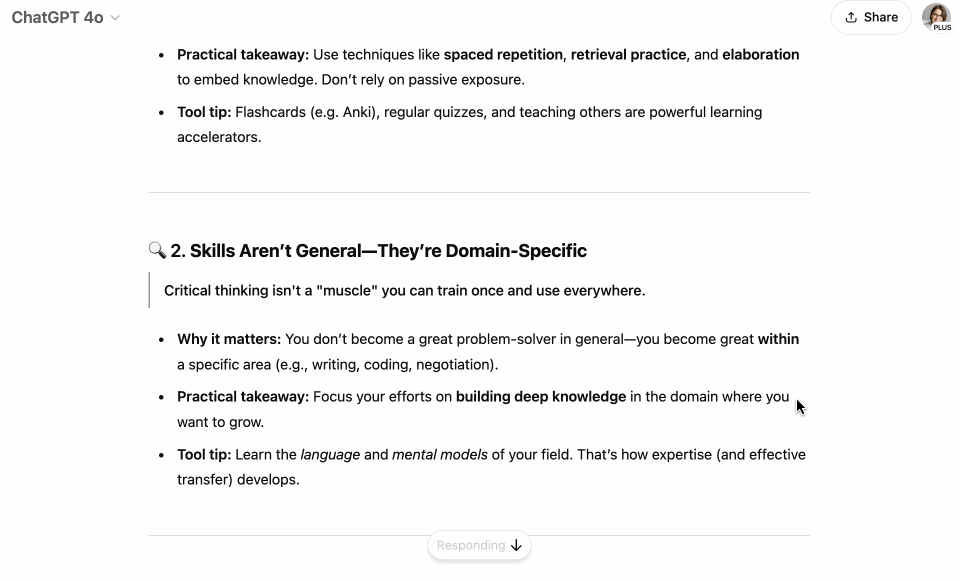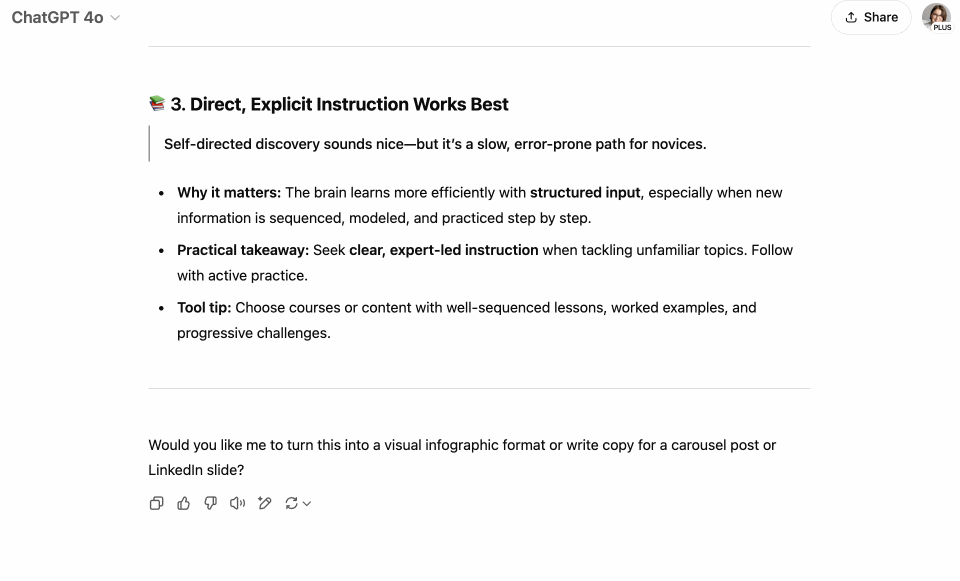
If I were to create an infographic of the attached PDF with the most useful and helpful ideas for lifelong learners and busy professionals. Focus on insights that are practical, actionable, time-saving, or directly contribute to skill development and knowledge application for this group. Which 3 core ideas would it entail? Here’s a screen recording of me running this prompt. The PDF I uploaded was a report on The Science of Learning by Trisha Jha.
Step 2: Create a brief for the infographic
Then, continue your conversation in the same chat. Here’s the prompt you can copy:
#task Generate a brief for Chat GPT 4o image creator for a visually compelling and highly intuitive infographic for the information you've just surfaced. The infographic should be designed for maximum clarity and memorability (knowledge retention). The aesthetic should be sophisticated minimalist, appearing professionally crafted by an expert information designer.
#restrictions
Layout & Style:
Format: Single-panel infographic.
Perspective: Consistent top-down ('flat lay') view for all elements.
Aesthetic: Clean, minimalist design with abundant white space on a pure white background. Focus on clarity, legibility, and visual flow.
Hierarchy: Clear visual hierarchy guiding the user logically through the recipe. Use typography and element size strategically.
Color Palette: Minimalist, likely monochromatic with subtle accent colors if necessary for clarity (e.g., for arrows or numbers), maintaining a professional feel.
Visual Cues: Use clean, universally understood icons for key actions within each step. Icons must be stylistically consistent.
Connectors: Use subtle dotted lines or clean, minimal arrows to show the flow from one step to the next, guiding the eye effortlessly.
Avoid decorative elements that don't serve an informational purpose.
Here’s my screen recording of running this prompt. I could’ve asked for edits — which I didn’t, as I found the initial output really good.
Step 3. Let GPT-4o’s image generator do its magic
Select (or write) “Create Image” and copy the brief you received in the chat. It’s important that you stay in the same chat window.
Here’s the result—first shot, no edits. I fact-checked it (based on my input: "What is the Science of Learning") and it’s accurate.
Further Examples Show This is Replicable
Here are 3 more infographics I created for some of my summaries of my favorite “learning” books based on the last 3 years.



Final Thoughts
It’s not just in the visuals GPT-4o creates. It’s in how those visuals help you think better. If you’re clarifying complex ideas or making an abstract concept feel intuitive, these prompts can serve as your learning leverage.
So the next time you hit a wall in understanding, don’t just re-read or overthink. Prompt differently. Visualize it. Iterate with GPT-4o like you would with a design partner. What you get back might just be the clearest version of your own thinking yet.
However, don’t forget that rigorous fact-checking is non-negotiable. Always verify the AI's interpretation and visual output against the original source, avoiding misleading oversimplification. The ultimate responsibility for the output's integrity lies with you.
Be mindful of copyright considerations regarding both the input material and the output visuals. Respect the rights of original creators and consult OpenAI's usage policies. Where possible, work with materials you have permission to use or focus on generating visuals based on your own synthesized understanding.
That said, ChatGPT can help you learn smarter. And maybe—just maybe—design ideas that stick long after the scroll.
Sources
Clark, J. M., & Paivio, A. (1991). Dual coding theory and education. Educational Psychology Review. (Foundation of Dual Coding)
Sweller, J. (1988). Cognitive load during problem solving: Effects on learning. Cognitive Science. (Foundation of Cognitive Load Theory)
Chi, M. T. H., Feltovich, P. J., & Glaser, R. (1981). Categorization and representation of physics problems by experts and novices. Cognitive Science. (On expert schemas)
OpenAI Blog: Introducing GPT-4o (Details on the model's capabilities) https://openai.com/index/introducing-4o-image-generation/
https://www.sydney.edu.au/news-opinion/news/2025/04/03/chatgpt-s-studio-ghibli-style-images-show-its-creative-power.html
https://petapixel.com/2025/03/26/images-in-chatgpt-ai-generator-openai/
Your brain processes visual and verbal info through separate channels. Pairing them (text + relevant image) creates stronger, faster recall pathways. Abstract ideas especially benefit. AI can generate precise, context-rich visuals on demand for any concept. This forces your brain to encode information twice—visually and verbally—embedding it deeper than text alone.
Our working memory is tiny. Learning stalls when it's overwhelmed. Effective learning minimizes irrelevant mental work ("extraneous load") and supports the effort needed to build understanding ("germane load"). AI can help turn dense text into clear diagrams, flowcharts, or concept maps. This reduces the strain of deciphering complex relationships from words alone, freeing up mental bandwidth to actually learn and build robust mental models (schemas).
I’m using the ChatGPT pro version.